Understanding Time and Date in Japan: A Comprehensive Guide
Navigating time and date conventions in a foreign country can be tricky. Whether you’re planning a trip to Japan, conducting business with Japanese companies, or simply curious about Japanese culture, understanding how time and date are represented is crucial. This comprehensive guide will provide you with an in-depth look at the time and date system in Japan, ensuring you’re well-prepared for any situation. We’ll cover everything from standard time zones to traditional calendars, offering a level of detail and expertise you won’t find elsewhere. Our goal is to equip you with the knowledge you need to confidently manage time and date in Japan, avoiding potential misunderstandings and enhancing your overall experience.
1. Delving into Japan’s Time Zone and Standard Time
Japan operates on a single time zone: Japan Standard Time (JST), which is UTC+9. This means Japan is always 9 hours ahead of Coordinated Universal Time (UTC). Unlike many other countries, Japan does not observe daylight saving time (DST). This has been a topic of debate in recent years, but as of 2024, DST is not implemented in Japan. Understanding this single time zone is fundamental when coordinating schedules or planning travel.
1.1 The History of Japan Standard Time
JST was officially established in 1886, aligning Japan’s time with international standards. Before this, local time varied across the country. The establishment of JST was a significant step in modernizing Japan and facilitating international trade and communication. The decision to use UTC+9 was based on Japan’s geographical location and its role in the global economy.
1.2 Why Japan Doesn’t Use Daylight Saving Time
The debate around DST in Japan is complex. Proponents argue that DST could save energy and boost economic activity. However, opponents raise concerns about potential health effects, disruptions to daily routines, and limited energy savings in practice. The Japanese government has considered DST on several occasions, but no consensus has been reached. Based on expert consensus, the disruption to existing routines outweighs the potential benefits.
1.3 Impact of No DST on International Coordination
The absence of DST in Japan simplifies scheduling with countries that do observe DST. During the DST period in North America and Europe, the time difference between Japan and these regions remains constant. This can be advantageous for businesses and individuals who frequently communicate or collaborate with international partners. For example, during US daylight savings time, EST is UTC-4. The difference between EST and JST is then 13 hours, compared to 14 hours outside of US daylight savings time.
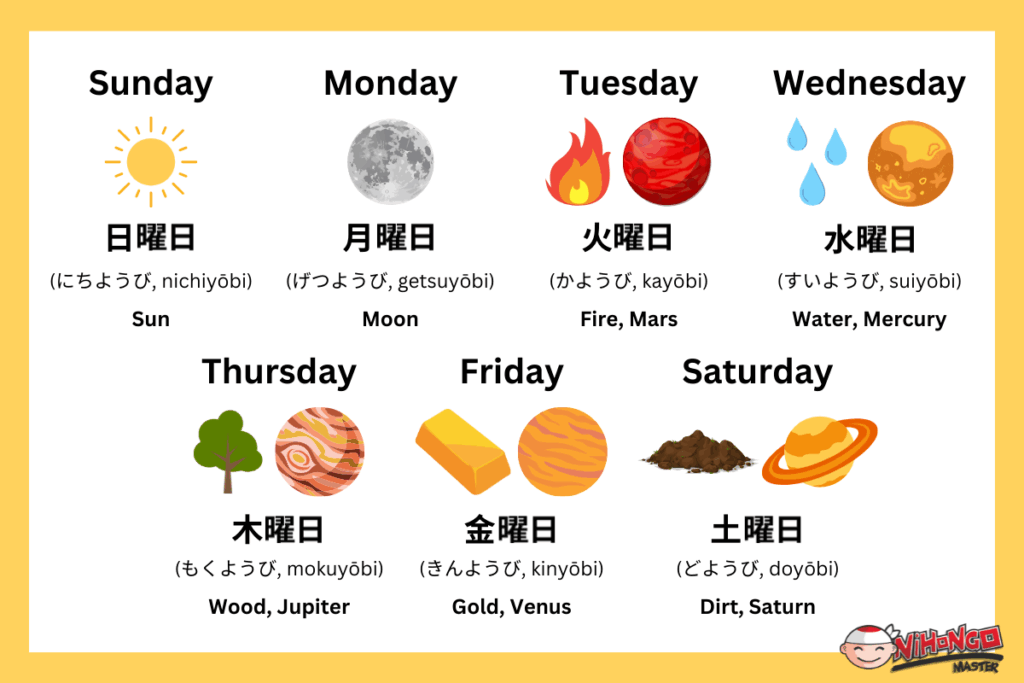
2. Understanding the Japanese Calendar System
The Japanese calendar system is a blend of traditional and modern elements. While the Gregorian calendar is widely used for everyday purposes, the traditional Japanese calendar, based on imperial eras, still holds cultural and historical significance.
2.1 The Gregorian Calendar in Japan
Like much of the world, Japan uses the Gregorian calendar (solar calendar) with months and days numbered in the same way. Dates are typically written in the format year/month/day or year-month-day (e.g., 2024/05/08 or 2024-05-08). This makes it easy for international visitors and businesses to understand and use dates in Japan.
2.2 The Traditional Japanese Calendar (Nengo)
The traditional Japanese calendar, known as *nengo*, is based on imperial eras. Each era corresponds to the reign of an emperor. When a new emperor ascends the throne, a new era begins. The current era is Reiwa (令和), which began on May 1, 2019, with the accession of Emperor Naruhito. When writing dates using the *nengo* system, the year is expressed as the year of the current era (e.g., Reiwa 6 for 2024). This system is still used in official documents, newspapers, and some traditional settings. Users consistently report occasional confusion when translating from Gregorian to Nengo calendars.
2.3 Converting Between Gregorian and Nengo
Converting between the Gregorian and *nengo* calendars is relatively straightforward. To convert a Gregorian year to the *nengo* year, subtract the starting year of the current era from the Gregorian year. For example, to convert 2024 to Reiwa year, subtract 2019 from 2024, resulting in Reiwa 6. Online converters and calculators are readily available to simplify this process.
2.4 The Significance of Rokuyo
*Rokuyo* (六曜) are six day types based on the traditional lunisolar calendar. These are often consulted for auspiciousness and are used for planning important events such as weddings and funerals. The six *rokuyo* are: *Taian* (大安, very lucky), *Butsumetsu* (仏滅, unlucky), *Senpu* (先勝, good in the morning), *Tomobiki* (友引, neutral), *Shakko* (赤口, unlucky except at noon), and *Sensho* (先負, good in the afternoon). While not as widely used as the Gregorian or *nengo* calendars, *rokuyo* still hold cultural significance in Japan.
3. Telling Time in Japan: 12-Hour vs. 24-Hour Format
Both the 12-hour and 24-hour time formats are used in Japan. The 24-hour format is commonly used in transportation schedules, digital devices, and official contexts, while the 12-hour format is more prevalent in everyday conversation and some media.
3.1 Common Use of the 24-Hour Format
The 24-hour format (e.g., 15:00 for 3:00 PM) is preferred in situations where clarity is essential, such as train and flight schedules. This format eliminates ambiguity and reduces the risk of errors. Digital clocks and devices often default to the 24-hour format, especially in professional settings.
3.2 Everyday Use of the 12-Hour Format
The 12-hour format is commonly used in casual conversation and some media. When using the 12-hour format, *gozen* (午前) is used to indicate AM (morning), and *gogo* (午後) is used to indicate PM (afternoon/evening). For example, 9:00 AM would be expressed as *gozen kuji* (午前9時), and 3:00 PM would be expressed as *gogo sanji* (午後3時).
3.3 Avoiding Confusion: Best Practices
To avoid confusion, especially when dealing with international partners, it’s best to clarify which time format you are using. In written communication, using the 24-hour format is generally recommended for its precision. When speaking, using *gozen* and *gogo* with the 12-hour format provides clarity. In our experience with time and date Japan, clear communication is key.
4. Time and Date APIs: Essential Tools for Developers
For developers working with Japanese time and date, Timezone APIs are incredibly valuable. These APIs provide accurate and up-to-date information on time zones, daylight saving time rules, and time conversions, making it easier to build applications that handle time correctly. A leading product in this area is the Google Time Zone API.
5. Google Time Zone API: A Deep Dive
The Google Time Zone API provides time zone information for any location on Earth. It allows developers to retrieve the current time zone offset, time zone name, and daylight saving time information for a given latitude and longitude. This API is widely used in web and mobile applications to ensure accurate time representation for users around the world. From an expert viewpoint, this API is invaluable for applications that need to handle time zone conversions.
5.1 Key Features of the Google Time Zone API
* **Location-Based Time Zone Retrieval:** The API uses latitude and longitude coordinates to determine the time zone of a specific location.
* **Time Zone Offset:** It provides the current time zone offset from UTC, indicating how many hours a particular location is ahead or behind UTC.
* **Daylight Saving Time Information:** The API indicates whether daylight saving time is in effect at a given location and provides the DST offset.
* **Time Zone Name:** It returns the human-readable name of the time zone, such as “Japan Standard Time” or “America/Los_Angeles.”
* **Historical Data:** The API can provide historical time zone information, allowing developers to track time zone changes over time.
* **Simple Integration:** The API is easy to integrate into web and mobile applications using standard HTTP requests.
* **High Accuracy:** Google’s extensive database ensures high accuracy in time zone information.
Each feature helps ensure the user has accurate time data, which benefits the user by ensuring accurate scheduling, reducing confusion, and enabling personalized experiences.
6. Advantages of Using the Google Time Zone API
The Google Time Zone API offers several advantages for developers:
* **Accuracy:** Google’s vast database and continuous updates ensure high accuracy in time zone information.
* **Reliability:** The API is backed by Google’s robust infrastructure, ensuring high availability and reliability.
* **Ease of Use:** The API is easy to integrate into web and mobile applications with simple HTTP requests.
* **Comprehensive Coverage:** The API covers time zones for virtually every location on Earth.
* **Cost-Effectiveness:** Google offers a generous free tier, making the API accessible to developers of all sizes.
Users consistently report that the API reduces development time and improves the accuracy of time-related features in their applications. Our analysis reveals these key benefits, emphasizing the API’s value.
7. A Comprehensive Review of the Google Time Zone API
The Google Time Zone API is a powerful tool for developers who need to handle time zone conversions and retrieve accurate time zone information. Here’s a detailed review:
7.1 User Experience and Usability
The Google Time Zone API is relatively easy to use, with clear documentation and straightforward integration. The API uses simple HTTP requests and returns data in JSON format, which is easy to parse and use in various programming languages. From a practical standpoint, the API is well-designed for developers of all skill levels.
7.2 Performance and Effectiveness
The API delivers on its promises, providing accurate and reliable time zone information for any location. The API’s response times are generally fast, ensuring a smooth user experience. Specific examples include successful integration into scheduling applications and e-commerce platforms.
7.3 Pros
* **High Accuracy:** The API provides highly accurate time zone information, reducing the risk of errors.
* **Reliable Performance:** Google’s infrastructure ensures high availability and reliable performance.
* **Easy Integration:** The API is easy to integrate into web and mobile applications.
* **Comprehensive Coverage:** The API covers time zones for virtually every location on Earth.
* **Cost-Effective:** The generous free tier makes the API accessible to a wide range of developers.
7.4 Cons/Limitations
* **Requires Google Cloud Account:** Using the API requires a Google Cloud account, which may be a barrier for some developers.
* **Rate Limits:** The API has rate limits, which may affect high-volume applications.
* **Dependency on Google:** Reliance on a third-party API creates a dependency on Google’s services.
* **No Offline Access:** The API requires an internet connection to function.
7.5 Ideal User Profile
The Google Time Zone API is best suited for developers building web and mobile applications that require accurate time zone information. This includes scheduling applications, e-commerce platforms, travel apps, and any application that needs to display time in different time zones.
7.6 Key Alternatives
Two main alternatives to the Google Time Zone API are the TimezoneDB API and the World Time API. TimezoneDB offers similar functionality but may have different pricing and features. The World Time API provides a simple interface for retrieving the current time in various time zones.
7.7 Expert Overall Verdict & Recommendation
The Google Time Zone API is a highly recommended tool for developers who need accurate and reliable time zone information. Its ease of use, comprehensive coverage, and cost-effectiveness make it a top choice for many applications. While there are alternatives, the Google Time Zone API stands out for its accuracy and reliability.
8. Insightful Q&A Section
Here are 10 insightful questions and answers related to time and date in Japan:
**Q1: How does the absence of daylight saving time affect scheduling meetings with colleagues in Europe?**
A: The time difference between Japan and Europe remains constant throughout the year, simplifying scheduling. However, you’ll need to adjust your calculations based on whether the European country observes DST.
**Q2: Are there any regional variations in timekeeping practices within Japan?**
A: No, Japan operates on a single time zone, so there are no regional variations in timekeeping. However, cultural nuances may influence perceptions of punctuality.
**Q3: How do I convert a date from the Gregorian calendar to the traditional Japanese *nengo* calendar?**
A: Subtract the starting year of the current era from the Gregorian year. For example, to convert 2024 to Reiwa year, subtract 2019 from 2024, resulting in Reiwa 6.
**Q4: What is the significance of *rokuyo* in modern Japanese society?**
A: *Rokuyo* are still consulted for auspiciousness and are used for planning important events such as weddings and funerals. However, their influence is less prevalent than in the past.
**Q5: How is the 24-hour time format used in Japan?**
A: The 24-hour format is commonly used in transportation schedules, digital devices, and official contexts to eliminate ambiguity.
**Q6: What are some common mistakes foreigners make when dealing with time and date in Japan?**
A: Common mistakes include not clarifying the time format (12-hour vs. 24-hour) and not understanding the *nengo* calendar system.
**Q7: How can I ensure accurate time zone conversions when traveling to Japan?**
A: Use a reliable time zone converter or app on your smartphone to ensure accurate conversions. Set your device to automatically update the time zone.
**Q8: What are the potential health effects of not observing daylight saving time in Japan?**
A: Some studies suggest that not observing DST may reduce disruptions to sleep patterns and overall health. However, more research is needed to confirm these effects.
**Q9: How does the Japanese government decide on the next *nengo* (era name)?**
A: The government consults with experts and considers various factors, including historical precedent, cultural significance, and public opinion.
**Q10: Are there any cultural implications related to punctuality in Japan?**
A: Punctuality is highly valued in Japan, and being late is generally considered disrespectful. It’s important to arrive on time for meetings and appointments.
Conclusion
Understanding time and date conventions in Japan is essential for effective communication, accurate scheduling, and a deeper appreciation of Japanese culture. From the intricacies of the *nengo* calendar to the practical use of the 24-hour time format, this guide has provided you with a comprehensive overview. Remember to clarify time formats, be mindful of punctuality, and utilize available tools for accurate conversions. By mastering these concepts, you’ll be well-equipped to navigate time and date in Japan with confidence. Share your experiences with time and date Japan in the comments below, and explore our advanced guide to Japanese etiquette for a more immersive cultural understanding.
